Tensor Parallel
1 Tensor Parallel Example
1.1 pytorch_tp.py 脚本
python
import os
import sys
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.distributed.tensor.parallel import (
parallelize_module,
ColwiseParallel,
RowwiseParallel,
)
from torch.distributed._tensor.device_mesh import init_device_mesh
from torch.nn.parallel import DistributedDataParallel as DDP
class ToyModel(nn.Module):
"""MLP based model"""
def __init__(self):
super(ToyModel, self).__init__()
self.in_proj = nn.Linear(10, 32)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.out_proj = nn.Linear(32, 5)
def forward(self, x):
return self.out_proj(self.relu(self.in_proj(x)))
def train(model, optimizer, train_step):
input = torch.randn(20, 10, device="cuda")
target = torch.randn(20, 5, device="cuda")
for i in range(train_step):
# For TP, input needs to be same across all TP ranks.
# Setting the random seed is to mimic the behavior of dataloader.
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(input)
loss = (output - target).var()
print(f"===============loss : {loss} \n")
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if __name__ == "__main__":
torch.manual_seed(45)
_world_size = int(os.environ["WORLD_SIZE"])
device_mesh = init_device_mesh(device_type="cuda", mesh_shape=(1, _world_size), mesh_dim_names=("dp", "tp")) # 在这里设置device
_rank = device_mesh.get_rank()
print(f"Starting PyTorch TP example on rank {_rank}.")
assert (
_world_size % 2 == 0
), f"TP examples require even number of GPUs, but got {_world_size} gpus"
tp_model = ToyModel().to("cuda").train()
# Custom parallelization plan for the model
tp_model = parallelize_module(
module=tp_model,
device_mesh=device_mesh["tp"],
parallelize_plan={
"in_proj": ColwiseParallel(),
"out_proj": RowwiseParallel(),
},
)
optimizer = torch.optim.AdamW(tp_model.parameters(), lr=0.05, foreach=True)
train(tp_model, optimizer, 10)1.2 运行指令
shell
torchrun --nnodes=1 --nproc-per-node=2 --master-addr=localhost --master-port=5972 pytorch_tp.py2 TP用到的主要数据结构及调度流程
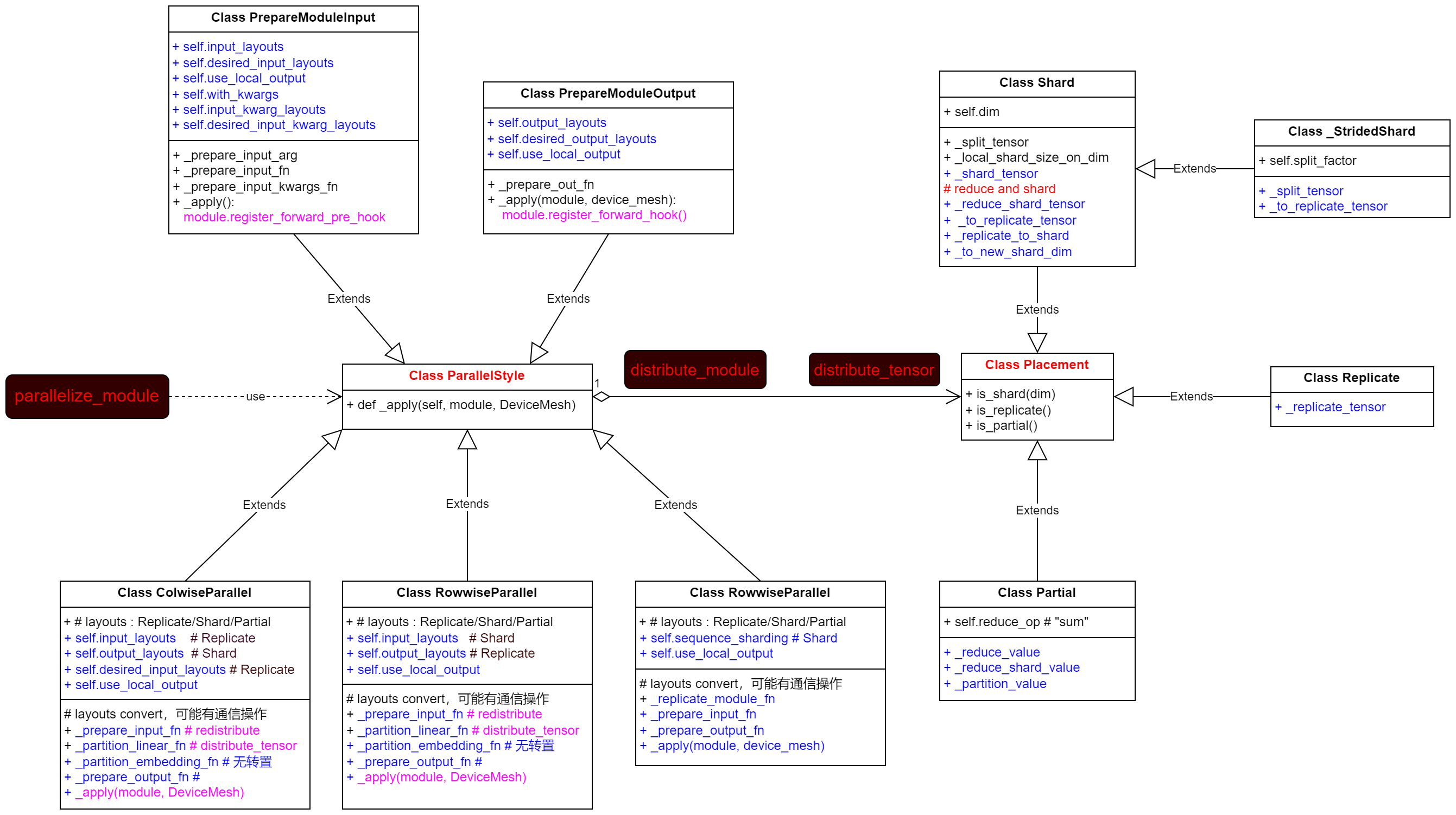
3 关键点阐述
- 用户使用 parallel_module 对常规模型进行warpper, 返回parallel后的模型;
- parallel_model 通过 distribute_model 调用每个sub-module 对应的 ParallelStyle 具体instance 的 _apply 方法来完成对tensor的切分和注册hook函数;
- 具体的切分函数在Placement 的具体实例 Shard/_StridedShard/Replica/Partial 内实现;
- ParallelStype instance 的 method 里通过 distribute_tensor 调度到 Placement的类方法里;
- 第一次算子调度时tensor的类型时DTensor, 这样根据pytorch 的dispatcher 机制,会触发到dispatchKey 为 python的调度;
- 第二次调度所有算子会到 DTensor 的 torch_dispatch;
- torch_dispatch 会调度到torch.distributed.tensor._dispatch.OpDispatcher.dispatch(func, args, kwargs);
- 在OpDispatcher.dispatch里将DTensor 转换为 local tensor;
- 最后在dispatch 里调用torch._ops.OpOverload 来执行算子.
4 Pytorch 源码详解
4.1 parallelize module
注意: 这里比较重要的是 parallelize_plan, 根据这个plan 我们递归的将model的不同部分进行parallelize.
python
def parallelize_module( # type: ignore[return]
module: nn.Module,
device_mesh: DeviceMesh,
parallelize_plan: Union[ParallelStyle, Dict[str, ParallelStyle]],
) -> nn.Module:
"""
Apply Tensor Parallelism in PyTorch by parallelizing modules or sub-modules based on a user-specified plan.
We parallelize module or sub_modules based on a parallelize_plan. The parallelize_plan contains
:class:`ParallelStyle`, which indicates how user wants the module or sub_module
to be parallelized.
User can also specify different parallel style per module fully qualified name (FQN).
Note that ``parallelize_module`` only accepts a 1-D :class:`DeviceMesh`, if you have a 2-D or N-D :class:`DeviceMesh`,
slice the DeviceMesh to a 1-D sub DeviceMesh first then pass to this API(i.e. ``device_mesh[\"tp\"]``)
Args:
module (:class:`nn.Module`):
Module to be parallelized.
device_mesh (:class:`DeviceMesh`):
Object which describes the mesh topology
of devices for the DTensor.
parallelize_plan (Union[:class:`ParallelStyle`, Dict[str, :class:`ParallelStyle`]]):
The plan used to parallelize the module. It can be either a
:class:`ParallelStyle` object which contains how
we prepare input/output for Tensor Parallelism or it can be a
dict of module FQN and its corresponding :class:`ParallelStyle` object.
Return:
A :class:`nn.Module` object parallelized.
Example::
>>> # xdoctest: +SKIP("distributed")
>>> from torch.distributed.tensor.parallel import parallelize_module, ColwiseParallel
>>> from torch.distributed.device_mesh import init_device_mesh
>>>
>>> # Define the module.
>>> m = Model(...)
>>> tp_mesh = init_device_mesh("cuda", (8,))
>>> m = parallelize_module(m, tp_mesh, {"w1": ColwiseParallel(), "w2": RowwiseParallel()})
>>>
.. note:: For complex module architecture like Attention, MLP layers, we recommend composing
different ParallelStyles together (i.e. ``ColwiseParallel`` and ``RowwiseParallel``) and pass
as a parallelize_plan, to achieves the desired sharding computation.
"""
torch._C._log_api_usage_once("torch.distributed.tensor.parallel.parallelize_module")
_validate_tp_mesh_dim(device_mesh)
# instantiate a TP RNG state tracker if it's not there
if is_rng_supported_mesh(device_mesh) and not isinstance(
random._rng_tracker, TensorParallelRNGTracker
):
random._rng_tracker = TensorParallelRNGTracker(device_mesh.device_type)
# TODO: we should allow user to pass in the default seed from a config
random._rng_tracker._manual_seed(device_mesh, base_seed=1234)
# By default we execute random ops in non-tensor-parallel region. If users want
# to execute in tensor-parallel region, they can manually set this field to True
# after parallelizing the model.
random._rng_tracker.distribute_region_enabled = False
if isinstance(parallelize_plan, ParallelStyle):
return parallelize_plan._apply(module, device_mesh)
elif isinstance(parallelize_plan, dict):
for module_path, parallelize_style in parallelize_plan.items():
path_splits = module_path.split(".")
if len(path_splits) == 0:
raise ValueError(
"Expect module path to be non-empty, but got empty string!"
)
while path_splits:
atom = path_splits.pop(0)
matched_children = filter(
# `t[0]` is child name
lambda t: fnmatch(t[0], atom),
module.named_children(),
)
# apply the plan to all matched submodules
for _, submodule in matched_children:
if path_splits:
# we haven't reached the leaf, apply in dict style
leaf_path = ".".join(
path_splits
) # rest of the path after `atom`
parallelize_module(
submodule, device_mesh, {leaf_path: parallelize_style}
)
else:
# otherwise, directly apply style to this submodule
parallelize_module(submodule, device_mesh, parallelize_style)
return module
else:
raise TypeError( # pyre-ignore[7]
"Expect Union[ParallelStyle, Dict[str, ParallelStyle]] for"
f" parallelize_plan, {type(parallelize_plan)} found!"
)4.2 ParallelStyle
python
class ParallelStyle(ABC):...
class ColwiseParallel(ParallelStyle):
def _prepare_input_fn(
input_layouts, desired_input_layouts, mod, inputs, device_mesh
):
def _partition_linear_fn(self, name, module, device_mesh):
def _partition_embedding_fn(self, name, module, device_mesh):
@staticmethod
def _prepare_output_fn(output_layouts, use_local_output, mod, outputs, device_mesh):
def _apply(self, module: nn.Module, device_mesh: DeviceMesh) -> nn.Module:
class RowwiseParallel(ParallelStyle):
def __init__(
self,
*,
input_layouts: Optional[Placement] = None,
output_layouts: Optional[Placement] = None,
use_local_output: bool = True,
):
@staticmethod
def _prepare_input_fn(
input_layouts, desired_input_layouts, mod, inputs, device_mesh
):
def _partition_linear_fn(self, name, module, device_mesh):
def _partition_embedding_fn(self, name, module, device_mesh):
@staticmethod
def _prepare_output_fn(output_layouts, use_local_output, mod, outputs, device_mesh):
def _apply(self, module: nn.Module, device_mesh: DeviceMesh) -> nn.Module:
class SequenceParallel(ParallelStyle):
def __init__(self, *, sequence_dim: int = 1, use_local_output: bool = False):
def _replicate_module_fn(
self, name: str, module: nn.Module, device_mesh: DeviceMesh
):
def _prepare_input_fn(sequence_sharding, mod, inputs, device_mesh):
def _prepare_output_fn(use_local_output, mod, outputs, device_mesh):
def _apply(self, module: nn.Module, device_mesh: DeviceMesh) -> nn.Module:
class PrepareModuleInput(ParallelStyle):
def __init__(
self,
*,
input_layouts: Optional[Union[Placement, Tuple[Optional[Placement]]]] = None,
desired_input_layouts: Optional[
Union[Placement, Tuple[Optional[Placement]]]
] = None,
input_kwarg_layouts: Optional[Dict[str, Placement]] = None,
desired_input_kwarg_layouts: Optional[Dict[str, Placement]] = None,
use_local_output: bool = False,
):
def _prepare_input_arg(
self,
input: Any,
mesh: DeviceMesh,
input_layout: Optional[Placement],
desired_layout: Optional[Placement],
):
def _prepare_input_fn(self, inputs, device_mesh):
def _prepare_input_kwarg_fn(self, inputs, kwarg_inputs, device_mesh):
def _apply(self, module: nn.Module, device_mesh: DeviceMesh) -> nn.Module
class PrepareModuleOutput(ParallelStyle):
def __init__(
self,
*,
output_layouts: Union[Placement, Tuple[Placement]],
desired_output_layouts: Union[Placement, Tuple[Placement]],
use_local_output: bool = True,
):
def _prepare_out_fn(self, outputs, device_mesh):
def _apply(self, module: nn.Module, device_mesh: DeviceMesh) -> nn.Module:4.3 distributed_tensor (partition tensor)
针对input linear embedding output 的处理都有专门的函数:
python
def _partition_embedding_fn(self, name, module, device_mesh):
# rowwise shard embedding.weight is Shard(0)
for name, param in module.named_parameters():
dist_param = nn.Parameter(distribute_tensor(param, device_mesh, [Shard(0)]))
module.register_parameter(name, dist_param) # 将dist_param 注册到module中其中核心的distribute_tensor将param 根据Placement转换为DTensor
python
def distribute_tensor(
tensor: torch.Tensor,
device_mesh: Optional[DeviceMesh] = None,
placements: Optional[Sequence[Placement]] = None,
) -> DTensor:
"""
Distribute a leaf ``torch.Tensor`` (i.e. nn.Parameter/buffers) to the ``device_mesh`` according
to the ``placements`` specified. The rank of ``device_mesh`` and ``placements`` must be the
same. The ``tensor`` to distribute is the logical or "global" tensor, and the API would use
the ``tensor`` from first rank of the DeviceMesh dimension as the source of truth to perserve
the single-device semantic. If you want to construct a DTensor in the middle of the Autograd
computation, please use :meth:`DTensor.from_local` instead.
Args:
tensor (torch.Tensor): torch.Tensor to be distributed. Note that if you
want to shard a tensor on a dimension that is not evenly divisible by
the number of devices in that mesh dimension, we use ``torch.chunk``
semantic to shard the tensor and scatter the shards. The uneven sharding
behavior is experimental and subject to change.
device_mesh (:class:`DeviceMesh`, optional): DeviceMesh to distribute the
tensor, if not specified, must be called under a DeviceMesh context
manager, default: None
placements (List[:class:`Placement`], optional): the placements that
describes how to place the tensor on DeviceMesh, must have the same
number of elements as ``device_mesh.ndim``. If not specified, we will
by default replicate the tensor across the ``device_mesh`` from the
first rank of each dimension of the `device_mesh`.
Returns:
A :class:`DTensor` or ``XLAShardedTensor`` object.
.. note::
When initialize the DeviceMesh with the ``xla`` device_type, ``distribute_tensor``
return `XLAShardedTensor` instead. see `this issue <https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/92909>`__
for more details. The XLA integration is experimental and subject to change.
"""
torch._C._log_api_usage_once("torch.dtensor.distribute_tensor")
# get default device mesh if there's nothing specified
device_mesh = device_mesh or _mesh_resources.get_current_mesh()
device_type = device_mesh.device_type
if device_type == "xla":
try:
# call PyTorch/XLA SPMD for `xla` backend type device mesh.
# This returns XLAShardedTensor
from torch_xla.distributed.spmd import ( # type:ignore[import]
xla_distribute_tensor,
)
return xla_distribute_tensor(
tensor, device_mesh, placements
) # type:ignore[return-value]
except ImportError as e:
msg = "To use DTensor API with xla, you must install the torch_xla package!"
raise ImportError(msg) from e
# instantiate a RNG tracker if haven't. By default DTensor uses an
# OffsetBasedRNGTracker to perform random operators.
# TODO: the value assignment to global variable is not the ideal solution
# we can replace it in future.
if not random._rng_tracker and is_rng_supported_mesh(device_mesh):
random._rng_tracker = OffsetBasedRNGTracker(device_type)
if not tensor.is_leaf:
raise RuntimeError(
"`distribute_tensor` should be used to distribute leaf tensors! but found non-leaf tensor!"
)
# convert tensor to the corresponding device type if it's not in that device type
if device_type != tensor.device.type and not tensor.is_meta:
tensor = tensor.to(device_type)
# set default placements to replicated if not specified
if placements is None:
placements = [Replicate() for _ in range(device_mesh.ndim)]
if len(placements) != device_mesh.ndim:
raise ValueError(
f"`placements` must have the same length as `device_mesh.ndim`! "
f"Found placements length: {len(placements)}, and device_mesh.ndim: {device_mesh.ndim}."
)
if isinstance(tensor, DTensor):
# if the tensor is already a DTensor, we need to check:
# 1. if the we can further shard this DTensor if the two device mesh belong to
# the same parenet mesh and further sharding is possible.
# 2. check if device mesh and placements are the same
if tensor.device_mesh != device_mesh:
raise ValueError(
f"Cannot distribute a DTensor with device mesh {tensor.device_mesh} "
f"to a different device mesh {device_mesh}."
)
if tensor.placements != tuple(placements):
raise ValueError(
f"Cannot distribute a DTensor with placements {tensor.placements} "
f"to a different placements {placements}. do you want to call "
f"`redistribute` instead?"
)
return tensor
local_tensor = tensor.detach()
# TODO(xilun): address sharding order
# distribute the tensor according to the placements.
placements = list(placements)
for idx, placement in enumerate(placements):
if placement.is_shard():
placement = cast(Shard, placement)
if placement.dim < 0:
# normalize shard placement dim
placement = Shard(placement.dim + tensor.ndim)
placements[idx] = placement
local_tensor = placement._shard_tensor(local_tensor, device_mesh, idx)
elif placement.is_replicate():
placement = cast(Replicate, placement)
local_tensor = placement._replicate_tensor(local_tensor, device_mesh, idx)
else:
raise RuntimeError(
f"Trying to distribute tensor with unsupported placements {placement} on device mesh dimension {idx}!"
)
placements = tuple(placements)
assert local_tensor is not None, "distributing a tensor should not be None"
# detach the local tensor passed to DTensor since after the construction
# of DTensor, autograd would work on top of DTensor instead of local tensor
spec = DTensorSpec(
mesh=device_mesh,
placements=placements,
tensor_meta=TensorMeta(
shape=tensor.size(),
stride=tensor.stride(),
dtype=tensor.dtype,
),
)
return DTensor(
local_tensor.requires_grad_(tensor.requires_grad),
spec,
requires_grad=tensor.requires_grad,
)4.4 distributed_module
这个函数提供了三个方法来控制模块的参数、输入和输出, 返回一个Param 和 Buffer 全是DTensor的模型.
python
def distribute_module(
module: nn.Module,
device_mesh: Optional[DeviceMesh] = None,
partition_fn: Optional[Callable[[str, nn.Module, DeviceMesh], None]] = None,
input_fn: Optional[Callable[[nn.Module, Any, DeviceMesh], None]] = None,
output_fn: Optional[Callable[[nn.Module, Any, DeviceMesh], None]] = None,
) -> nn.Module:
"""
This function expose three functions to control the parameters/inputs/outputs of the module:
1. To perform sharding on the module before runtime execution by specifying the
``partition_fn`` (i.e. allow user to convert Module parameters to :class:`DTensor`
parameters according to the `partition_fn` specified).
2. To control the inputs or outputs of the module during runtime execution by
specifying the ``input_fn`` and ``output_fn``. (i.e. convert the input to
:class:`DTensor`, convert the output back to ``torch.Tensor``)
Args:
module (:class:`nn.Module`): user module to be partitioned.
device_mesh (:class:`DeviceMesh`): the device mesh to place the module.
partition_fn (Callable): the function to partition parameters (i.e. shard certain
parameters across the ``device_mesh``). If ``partition_fn`` is not specified,
by default we replicate all module parameters of ``module`` across the mesh.
input_fn (Callable): specify the input distribution, i.e. could control how the
input of the module is sharded. ``input_fn`` will be installed as a module
``forward_pre_hook`` (pre forward hook).
output_fn (Callable): specify the output distribution, i.e. could control how the
output is sharded, or convert it back to torch.Tensor. ``output_fn`` will be
installed as a module ``forward_hook`` (post forward hook).
Returns:
A module that contains parameters/buffers that are all ``DTensor`` s.
.. note::
When initialize the DeviceMesh with the ``xla`` device_type, ``distribute_module``
return nn.Module with PyTorch/XLA SPMD annotated parameters. See
`this issue <https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/92909>`__
for more details. The XLA integration is experimental and subject to change.
"""
torch._C._log_api_usage_once("torch.dtensor.distribute_module")
device_mesh = device_mesh or _mesh_resources.get_current_mesh()
device_type = device_mesh.device_type
if device_type == "xla":
try:
# This function annotates all module parameters for auto-partitioning with
# PyTorch/XLA SPMD or explicitly partition to :class:`XLAShardedTensor` parameters
# according to the `partition_fn` specified.
from torch_xla.distributed.spmd import ( # type:ignore[import]
xla_distribute_module,
)
return xla_distribute_module(
module, device_mesh, partition_fn, input_fn, output_fn
) # type:ignore[return-value]
except ImportError as e:
msg = "To use DTensor API with xla, you must install the torch_xla package!"
raise ImportError(msg) from e
def replicate_module_params_buffers(m: nn.Module, mesh: DeviceMesh) -> None:
# This function loop over the immediate module parameters and
# buffers, replicate all non DTensor params/buffers to DTensor
# parameters/buffers, if they have not been partitioned in the
# partition_fn, we can't easily use `module._apply` here
# because we don't know what happened inside partition_fn as
# user could do anything, i.e. install hooks, and we want to
# preserve those.
full_replicate = [Replicate()] * mesh.ndim
for key, param in m._parameters.items():
if param is not None and not isinstance(param, DTensor):
m.register_parameter(
key,
nn.Parameter(distribute_tensor(param.data, mesh, full_replicate)),
)
for key, buffer in m._buffers.items():
if buffer is not None and not isinstance(buffer, DTensor):
m._buffers[key] = distribute_tensor(buffer, mesh, full_replicate)
if partition_fn is None:
# if partition_fn not specified, we by default replicate
# all module params/buffers
for name, submod in module.named_modules():
replicate_module_params_buffers(submod, device_mesh)
else:
# apply partition_fun to submodules
for name, submod in module.named_modules():
partition_fn(name, submod, device_mesh)
replicate_module_params_buffers(submod, device_mesh)
# register input_fn as module forward pre hook
if input_fn is not None:
# check the input_fn signature
num_args = len(inspect.signature(input_fn).parameters)
if num_args == 2:
# input_fn only takes in inputs and device mesh
warnings.warn(
"Deprecating input_fn that takes two arguments (inputs, device_mesh), "
"please use input_fn that takes in (module, inputs, device_mesh) instead!",
FutureWarning,
stacklevel=2,
)
module.register_forward_pre_hook(lambda _, inputs: input_fn(inputs, device_mesh)) # type: ignore[call-arg]
elif num_args == 3:
# input_fn takes in module, inputs, device mesh
module.register_forward_pre_hook(
lambda mod, inputs: input_fn(mod, inputs, device_mesh)
)
else:
raise ValueError(
f"input_fn should take in 3 arguments, but got {num_args} arguments!"
)
# register output_fn as module forward hook
if output_fn is not None:
num_args = len(inspect.signature(output_fn).parameters)
if num_args == 2:
# output_fn only takes in outputs and device mesh
warnings.warn(
"Deprecating output_fn that takes two arguments (inputs, device_mesh), "
"please use output_fn that takes in (module, inputs, device_mesh) instead!",
FutureWarning,
stacklevel=2,
)
module.register_forward_hook(
lambda mod, inputs, outputs: output_fn(outputs, device_mesh) # type: ignore[call-arg]
)
elif num_args == 3:
module.register_forward_hook(
lambda mod, inputs, outputs: output_fn(mod, outputs, device_mesh)
)
else:
raise ValueError(
f"output_fn should take in 3 arguments, but got {num_args} arguments!"
)
return module5 Torchtitan 中 TP 的应用
5.1 对 embedding-norm-output进行parallel
python
"""Apply tensor parallelism."""
# 1. Parallelize the embedding and shard its outputs (which are the first
# transformer block's inputs)
# 2. Parallelize the root norm layer over the sequence dim
# 3. Parallelize the final linear output layer
parallelize_module(
model,
tp_mesh,
{
"tok_embeddings": RowwiseParallel(
input_layouts=Replicate(),
output_layouts=Shard(1),
),
"norm": SequenceParallel(),
"output": ColwiseParallel(
input_layouts=Shard(1),
output_layouts=Shard(-1) if loss_parallel else Replicate(),
use_local_output=not loss_parallel,
),
},
)5.2 对 其他layer进行parallel
python
for layer_id, transformer_block in model.layers.items():
layer_plan = {
"attention_norm": SequenceParallel(),
"attention": prepare_module_input(
input_layouts=(Shard(1), None),
desired_input_layouts=(Replicate(), None),
),
"attention.wq": colwise_parallel(),
"attention.wk": colwise_parallel(),
"attention.wv": colwise_parallel(),
"attention.wo": rowwise_parallel(output_layouts=Shard(1)),
"ffn_norm": SequenceParallel(),
"feed_forward": prepare_module_input(
input_layouts=(Shard(1),),
desired_input_layouts=(Replicate(),),
),
"feed_forward.w1": colwise_parallel(),
"feed_forward.w2": rowwise_parallel(output_layouts=Shard(1)),
"feed_forward.w3": colwise_parallel(),
}
parallelize_module(
module=transformer_block,
device_mesh=tp_mesh,
parallelize_plan=layer_plan,
)